Home
A comprehensive resource for safe and responsible laser use
US: Teen stares into laser pointer, has retinal damage
The unnamed teen initially had vision loss for several minutes due to flashblindness (looking into a bright light).
Five months later the boy went to an Ohio State University ophthalmologist due to continually-blurred vision with partial loss of vision in his right eye. Vision tests showed his left eye vision was normal. But if looking at text with his right eye, a single letter would be missing. When using only his left eye, or when using both eyes together, he could see the missing letter.
A standard clinical exam showed lesions in both eyes that were diagnosed as lesions in the macula, the area within the retina that we use for our central vision. The macula has the most and densest packing of light-detecting cones.
Tests done six months after the first doctor visit showed "marked improvement" in both eyes.
Further analysis was done with a custom-built adaptive optics optical coherence tomography scanning laser ophthalmoscope that is only one of five in the United States. This gives a very high-resolution view of the retina — much better than the human eye or more conventional retinal imaging techniques.
The AO-OCT-SLO image taken 11 months after the laser exposure showed damage to some of the macular cones. The ophthalmologist said "There's just nothing left there. The affected areas are devoid of cones."
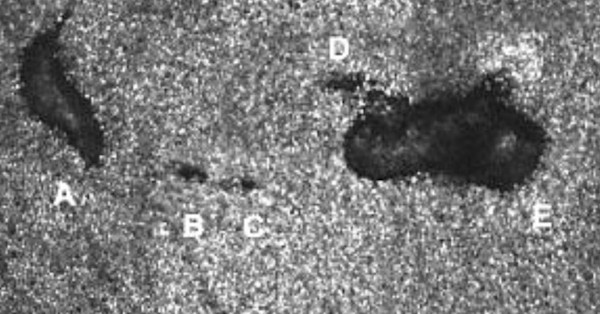
AO-OCT-SLO image of lesions A through E with small sites of cone loss (B, C, and D) in the teen's right eye. Each white dot is an individual cone cell, which is about 1/20th the width of a human hair. There are around six to seven million cones in the retina. Lesions A and E are about as wide as two hairs; lesions B-D are less than the width of a hair. Image source: Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. / Ohio State University
Another AO-OCT-SLO image taken nine months later showed the lesions decreased in size, from 3.7% to 23.8% compared to the first image. "However, the longer-term prognosis is likely permanent scarring," according to the report.
Original report in Retinal Cases & Brief Reports, summarized in an Ohio State News story. Other stories about this appeared in Science Alert and Interesting Engineering,
US: Indianapolis teen injured by laser pointer five years ago shares story
Vanderpool told his story in June 2018, to try to warn others to be careful about laser pointers. He said “We watched Star Wars and they had laser guns so we really didn’t know how dangerous it was.”
While he still has unspecified damage, treatment helped to repair much of the damage.
According to a news story, “the Indiana Academy of Ophthalmology and the Indiana State Medical Association are working on a resolution to deal with the laser pointer issue. They hope to release their findings by the end of September [2018].”
From RTV6 The Indy Channel
Commentary from LaserPointerSafety.com: Star Wars depicts lasers as weapons — not as toys. People die or are severely injured by the laser blasters and laser-like lightsabers. It is not clear how someone who watches Star Wars would not understand that lasers are dangerous — at least, as used in Star Wars.
Japan: Boy who routinely stared into a laser pointer develops lesion in one eye
At the age of 11, he had normal 20/20 (1.0) vision in the left eye, but 20/100 vision (0.20) in the right. Examination of the right eye showed a yellow lesion or fibrous tissue surrounded by a subretinal hemorrhage in the right macula. At age 13, examination showed the lesion was leaking on fluorescein angiography. At age 14, there was no change.
The doctors elected not to perform any treatment due to the patient’s age and mental condition.
From “Choroidal Neovascularization in a Child Following Laser Pointer-Induced Macular Injury”, Fujinami, K., Yokoi, T., Hiraoka, M. et al. Japanese Journal of Ophthalmology November 2010, Vol. 54, Issue 6, pp 631-633 (2010) 54: 631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-010-0876-z First online January 21 2011.
Greece: 9-year-old "repeatedly gazing" into laser causes hole in his eye
The most serious injury that the boy caused was a large hole in his macula, shown with the yellow arrows.
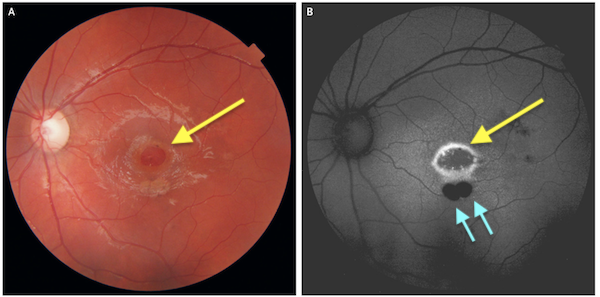
Two other areas of injury were not immediately visible in a funduscopic exam of the retina (photo A, using ordinary white light) but were clearly visible using fundus autofluorescence imaging (blue arrows in photo B, using a narrow wavelength of light). The round area to the left in both photos is the optic disc, a natural feature where the optic nerve begins — it is not laser damage.
The macula is where central vision occurs. The fact that the injury occurred in the macula indicates that the boy looked directly into the laser light with his left eye. Damage to the macula is serious as this area provides high resolution, color vision in the center of the visual field.
The injury reduced the boy’s vision to 20/100 in the injured left eye; his right eye remained at 20/20. The boy’s ophthalmologists felt the hole was too large and too much time had passed since the injury for surgery. (The doctors suspected that the boy had injured his eye at least a year earlier.) Because surgery might make things worse, causing a cataract without improving the macula, they “favored conservative management.”
There was no improvement in vision even 1 1/2 years after the injury was first presented to the ophthalmologists.
The power of the laser pointer, and other details of the incident, were not described in the one-paragraph report published June 21 2018. One of the authors told CNN the boy’s father “had bought the laser as a toy from a street merchant.”
From the New England Journal of Medicine (N Engl J Med 2018; 378:2420, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMicm1714488) Authors: Sofia Androudi, M.D., Ph.D., and Eleni Papageorgiou, M.D., Ph.D. Additional reporting by CNN. This story was picked up by many other news sites around the world.
UK: 12-year-old has permanent eye damage from reflected laser pointer beam
An optometrist who examined the boy said “It was clear after taking a close look at Carlo’s eyes that he had suffered some sort of damage. I could see there were slight burns to the surface of the eye [cornea] and the retina, the light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, had been damaged.”
According to the optometrist, the boy is likely to need glasses when he is older due to the “irreversible” damage.
Carlo’s mother said “I had no idea laser pens could do so much damage to the eyes. If we had known, we’d never have let him buy one. The damage was slight when it was detected so Carlo hadn’t complained of any issues, but thank goodness it got picked up when it did.”
From the Leicester Mercury and the Express
US: Study examines four laser-caused eye injuries in children, at one medical practice
In a separate interview, one of the authors, ophthalmologist Dr. David Almeida, said these cases are “happening more frequently…. It was previously thought this was a one-in-a-million event. It's still probably a rare-to-uncommon reaction, but it's not a never reaction.”
All four children had foveal laser burns. Three of the children had potentially permanent vision loss. These are the cases:
- A 12-year-old boy looked into a green laser pointer for about a minute. He had decreased central vision in both eyes, with 20/20 vision in one eye and 20/30 in another. His vision and macular condition was found to be unchanged after 7 months.
- A 16-year-old teenager similarly had central vision loss in both eyes, after playing with a green laser pointer for about 30 seconds. He was first examined three days after the exposure, scars and atrophy were found on the retina. Two weeks later his vision has worsened. Visual acuity was 20/40 in both eyes with no improvement.
- A 9-year-old boy looked at the reflection of a green laser pointer in a mirror (essentially the same as a direct beam) for an unknown length of time. His vision was 20/50. He was treated with 1% prednisolone three times a day for two weeks. His vision improved to 20/30, but he still had “persistent abnormalities of the photoreceptors.”
- A 12-year-old boy looked into a red laser pointer for about 15 seconds. He had central vision loss, and 20/70 vision. He was given an injection of bevacizumab, which gradually improved his vision and symptoms. After 1 year, he had 20/20 vision.
The authors noted that laser pointers are more available, that users may not be aware of the dangers, and that some users may use pointers improperly.
Visible lasers less than 5 milliwatts (the U.S. legal standard for a laser to be marketed as a “pointer”) are considered to be generally safe due to the bright light reflex, which causes a person to blink and turn away from a bright light. So one question is why these children were injured by laser pointers.
One reason, according to the authors, is that “children increase their chance to retinal injury by staring at the laser beam without blinking or averting the eye for a prolonged duration.”
Another possible cause is that “the labeling of the power output of a laser point may be different from the device’s actual specifications.” They referred to a study of 122 laser pointers, where 90% of green pointers and 44% of red pointers were above the 5 milliwatt U.S. legal limit.
The study said that treatment options were “limited and also controversial.” Use of corticosteroids has shown “mixed results.” It may be enough to observe a patient over time, since many injuries will stabilize.
The authors recommended that laser pointer hazards “should be communicated to health professionals, school teachers, and guardians in an attempt to raise the public awareness of this emerging public health issue. Unsupervised use of these laser pointer devices among children should be discouraged, and there is a need for legislation to limit these devices in the pediatric population.”
From Retinal Injury Secondary to Laser Pointers in Pediatric Patients, Kunyong Xu, Eric K. Chin, Polly A. Quiram, John B. Davies, D. Wilkin Parke III and David R.P. Almeida, in Pediatrics; originally published online September 1, 2016; DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-1188. A general interest article summarizing the study, with additional comments from Almeida and another ophthalmologist, is at HealthDay.com. The abstract of the Pediatrics article is below; click the “Read More…” link.
Click to read more...
UK: Woman sentenced for illegal laser imports that injured boy's eyesight
Lynsey McClure had imported the lasers from a Chinese supplier who said they complied with U.K. regulations limiting laser pens to 1 milliwatt of power. Her brother, who was not charged, sold them in a stall during a school fair in December 2015. The headmaster asked her brother to stop selling the laser, but he continued.

Lynsey McClure
Jonathan Marshall, 7, purchased one of the lasers. It was later found to have an output of 127 milliwatts.
His mother said Jonathan was playing with it at home when the beam went into his eye for “a fraction of a second.” He has a retinal burn which interferes with his vision.
McClure pleaded guilty to nine product safety and consumer protection violations, including selling an unsafe product and failing to disclose the power of the laser.
The case appears to be the first where a person has been prosecuted for an illegal laser sale that led to an injury.
From the Sunday Times (subscription required to read the entire article) and the JC.com
Australia: Teen injures both eyes by looking into laser pointer
From a November 5 news account, it appears the injury occurred on Friday October 30 2015. The boy saw a general practitioner the following Monday, who then referred the teen to Ben Armitage, a Hobart (Tasmania) optometrist.
Armitage said the boy did not feel pain during the exposure, but he immediately lost visual acuity. “His vision is down to about 25 percent of what we call 20/20 vision and unfortunately at this stage it’s unlikely that vision is ever going to recover.”
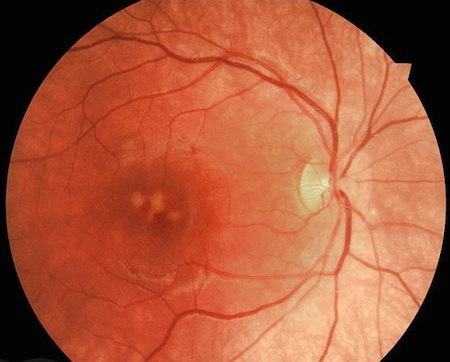
Retina of one of the teen’s two eyes that were damaged by a self-inflicted laser pointer exposure. The injury occurred near the macula. At the center of the macula is the fovea, responsible for sharp central vision.
The damaged area is still swollen; Armitage hopes that some vision may be restored when the swelling recedes.
An Optometry Tasmania spokesperson warned parents not to allow children unsupervised access to laser pointers “and, in fact, better off trying to warn them off because we’ve just seen in this particular case where the future lifestyle of this young person has been seriously affected.”
From ABC (Australia) News
Italy: Prosecutor investigating manslaughter charges in three cases of eye damage to children from laser pointers
The cases were reported in mid-September 2015 by the St. Ursula Ophthalmology Hospital in Bologna. One of the children was 10; the other two were 13.
The injuries were caused by laser pointers bought by their parents (in two cases) or grandmother (in the third case) in markets in Florence or Bologna. One child had a slight loss of vision, another had significant loss in both eyes, and a third has almost lost his sight and is legally blind.
A public prosecutor, Valter Giovannini, has opened an investigation for aggravated manslaughter against unknown assailants. This seems to indicate that in all three cases, the laser pointer bought by or for the children was used against them by another person.
As a result of the report, Carabinieri NAS (Nuclei Antisofisticazioni e Sanità or “Anti Fraud Squad”), a special police force operating under the Italian ministry of health, seized fifteen illegally-sold laser pointers.
The hospital warned the public not to purchase green laser pointers sold “on the street, in the stalls and fairs.” A spokesperson said higher-powered pointers such as those aimed at players in stadiums were to be avoided. Professional laser pointers used in lectures should not be a problem.
From Corriere di Bologna. Thanks to Alberto Kellner Ongaro for bringing this to our attention.
Austria: Pre-teen has "massive" damage from misusing laser pointer
A 12-year-old Austrian boy has suffered "massive and lasting" damage to his eyes after playing with a laser pointer, with his vision reduced by 60 percent, doctors said.
"We think that he was playing with a mirror and that the rays were reflected," said Yosuf El-Shabrawi, chief doctor at the Klagenfurt am Wörthersee clinic in Carinthia, southern Austria.
"His injuries cannot be treated. We can only hope that the worst of the injuries heal themselves and that his condition improves," El-Shabrawi said in a statement on Tuesday.
The boy's father bought the laser pointer on the Internet where it was advertised as a toy for playing with cats.
After a week the boy, named as Lukas, complained of a constant black mark in his field of vision.
The laser pointer in question was labelled as "Class 2" with an output under the European Union legal limit, but it lacked a so-called EN standardisation certificate, El-Shabrawi said.
AFP story on The Local, the Rakyat Post, iAfrica.com, and other news sources
Iceland: Teen injures both eyes playing with 90 mW laser pointer
The teen was treated at Landspitali University Hospital in Reykjavik. The head physician at the Department of Ophthalmology says the hospital has never seen such a severe case of laser pointer injury.
Click to read more...
UK: Journal report of five children injured by laser pens
According to the abstract, “Clinically, three children had an acute vitelliform-like maculopathy which resolved to leave sub-foveal retinal pigment epithelium changes with reduced vision. One case was complicated by a choroidal neovascular membrane.”
- Case 1 was of a nine-year-old boy who on December 22 2013 was tested with normal vision of 6/5 (U.S. 20/17 -- better than 20/20) but on December 26 complained of vision loss and was found to have 6/12 (20/40) in the left eye and 6/15 (20/50) in the right eye. The family said he was given a laser pointer as a “toy” and had been playing with it on Christmas Day. The child denied looking directly into the laser beam. The family had three laser pens: a 57 mW blue 405nm, a 42 mW green 532 nm, and a 72 mW red 650nm. All exceeded the British Standard of 5 mW for a Class 3R laser. The boy was prescribed steroids. Nine months after the initial complaint, the best corrected vision was 6/9.5 (20/32), and optical coherence tomography showed persistent outer retinal layer disruption at the fovea. [The boy was later identified in press coverage as William Jackson, from Wadsley. Details are at The Star.]
- Case 2 was of an 11-year-old boy. He had decreased vision in both eyes of 6/7.5 (20/25). Eight weeks later he had sub-foveal retinal pigment epithelium changes. His vision was 6/12 (20/40) in the right eye and 6/15 (20/50) in the left eye. He said that a friend had aimed a laser into both of his eyes before the decreased vision occurred. The doctors were not able to examine what they characterized as the laser “toy”.
- Case 3 was of a 15-year-old girl. She aimed a laser pen into both eyes for 30 seconds. The next day she had scotomas (vision loss or spots) in both eyes. Her right eye was 6/7.5 (20/25) and her left eye was 6/6 (20/20). Upon examination, a vitelliform-like maculopathy (abnormality in the macula or central vision area) was seen. She did not return for follow-up visits.
- Case 4 was of an 8-year-old boy who had reduced vision of 6/12 (20/40) in his right eye, and normal vision of 6/6 (20/20) in his left eye. The right fovea was seen to have retinal pigment epithelial changes “consistent with laser burns.” The boy admitted he had played with a laser pointer a few months before, but said he did not point it directly at his eye.
- Case 5 was of a 13-year-old boy who had noticed declining vision in his right eye. It was found to be 6/36 (20/120); his left eye was 6/6 (20/20). He admitted aiming a laser pointer into his right eye. A fibrosed choroidal neovascular membrane was found at the right fovea.
The authors noted that “The retinal damage reported following such injuries is variable. This is due to variety of laser powers and wavelengths as well as ocular factors such as fundal pigmentation, blink responses, pupil size, and proximity of the laser burn to the fovea. Assessment of alleged laser eye injury requires accurate history and examination. Treatment for such laser retinal injuries is uncertain. Oral corticosteroids are sometimes administered.”
The authors stated that some laser devices are marketed as “toys”. They said they are aware of other children in the U.K. with retinal injuries from imported laser pointers. They conclude: “We suggest that children should not be given laser pointers as toys.”
From “‘Toy’ laser macular burns in children”, in Eye (2014) 1-4, by N. Raoof, TKJ Chan, NK Rogers, W Abdullah, I Haq, SP Kelly and FM Quhill. A downloadable PDF version is here. A story from the Bolton News gives some additional comments from author SP Kelly.
Spain: Woman permanently injured by laser pointer bought in Shanghai
The injury to her fovea is permanent. In a machine-translated statement, she said “All fuzzy horrors bothers me the light. I sense what I see on the screen, but I can not really read and, of course, I dare not drive.”
The clinic says this is the first case it has seen of permanent retinal damage by a laser pointer.
The woman’s husband purchased three lasers in a tourist area of Shanghai, for €30 (USD $40). One emitted a red beam, one a blue beam and one a green beam. The spower was said to be between 500 and 6,000 milliwatts (1/2 to 6 watts). There were no user warnings on the laser.
The clinic believes the laser was not aimed directly in the eye, but was probably reflected off an object. While the article and machine-translation are not clear, it is possible that one or more of the lasers used a diffraction grating to create multiple “stars”. The article discusses lasers that “allow decorative figures with the laser on the surface” and then quotes the victim as saying “Ours were beautiful: creating colorful stars in the sky.”
From LaVanguardia.com. Original article in Spanish here; Google machine translation into English here. Thanks to Jose-Maria Silvestre on the LinkedIn Laser Safety Professionals group for bringing this to our attention.
Japan: Teen injured by LED pen "toy" held 40 seconds in his eye
A December 2006 incident has come to our attention. A 15-year-old Japanese boy suffered a retinal injury and visual loss after deliberately looking into a 5 mW violet (410 nm) light emitting diode for a total of about 40 seconds. The LED was in a pen was sold as a toy called “Secret Pen”. The toy appears to consist of an LED light which can excite ink that is invisible under ordinary light but which fluoresces under ultraviolet and near-UV light. The 410 nm wavelength caused photochemical damage to the retina.
According to a 2011 paper in Retinal Cases & Brief Reports, the LED was aimed into the teen’s eye from a distance of about 1 cm. It was held there for about 20 seconds as he deliberately stared into the light. This exposure was repeated the next day. About two weeks later, decreased vision (20/50 on the Snellen scale) was noted in the right eye.
Click to read more...
US: Teen partially blinded in one eye due to laser pointer
Retinal specialist Dr. Ramana Moorthy saw a “yellowish kind of spot here with yellow black flecks [that] shouldn’t be there.” She said the injury was permanent. The boy’s father said he considered the laser pointer a toy, and that he had no idea that laser light was dangerous. He said other parents should throw away their children’s pointers.
From WTHR.com. Thanks to Jochen Pernsteiner for bringing this to our attention.
World: Hobbyist injures self with 1 watt blue laser
(UPDATE March 14 2012: The hobbyist reported “I still have the blind spot, and was effectively told by the ophthalmologist that it would probably be there the rest of my life. That doesn't bother me TOO much, since it isn't very inhibiting.”)
.Click to read more...
New Zealand: Youth injury leads to calls for restrictions
Dr. Sharp and the boy’s mother both called for restrictions on laser pointers in New Zealand. The boy’s laser was purchased in Thailand for $15 while on a family holiday in January 2011. The date of the laser injury is not known.Click to read more...
Italy: Pre-school hit twice, parents fearful
The school board president says that the laser could only have come from apartments overlooking the school, but “we do not know if it is the act of a madman or a child struggling with a dangerous toy.” Police are searching for the perpetrator.
After the second incident, teachers lowered the blinds in the classroom. The report also notes other “increasing” incidents where laser pointers are used against pilots and football (soccer) goalies.
From Corriere Della Sera, “Laser negli occhi dei bimbi”. Thanks to Alberto Kellner Ongaro for bringing this to our attention.
Switzerland: Boy injures self with 150 mW pointer
An examination two weeks later showed injuries to both retinas. There was severe vision loss in the left eye and 20/50 vision in the right. His left eye was injected with ranibizumab which helped improve vision to 20/25 after four weeks. The right eye improved on its own to 20/32.
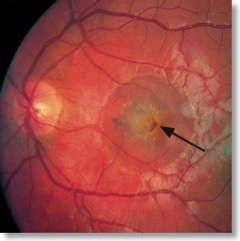
The left eye clearly shows damage from a self-inflicted exposure to a 150 mW green laser pointer.
The report appeared in a letter published September 9 2010 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
UK doctors: Laser pointer damages youth's eyes
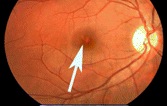
The burn site on the youth’s right eye