Home
A comprehensive resource for safe and responsible laser use
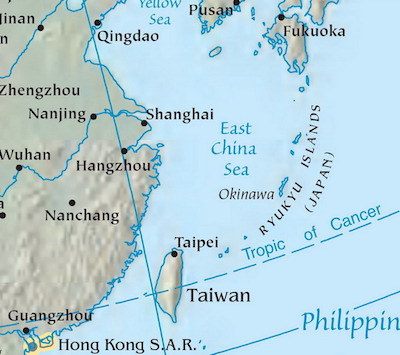
US & East China Sea: US officials say lasers have targeted military pilots in the East China Sea
U.S. officials said the low-level, harassing beams came from fishing vessels and from shore.
U.S. and Chinese military interests have had disputes in the East China Sea in recent years. However, there was no specific indication of whether there was malicious intent, or any organized effort behind the laser incidents. The officials speculated that the lasers could be directed by the Chinese government, or could be “disgruntled Chinese fishermen… who simply want to harass American pilots.”
A spokesperson for the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command said that flying procedures have not changed due to the laser incidents. She did say pilots are “employing” required laser eye protection.
A spokesperson for the Chinese Foreign Ministry called claims that China was responsible for the East China Sea lasers “groundless and sheer fabrications.”
According to news.com.au, “All aspects of the Chinese economy are state-controlled. And its fishing fleets are operated as a militia, working in close concert with Beijing’s navy as it seeks to assert its arbitrary claim to total control of the South and East China Seas…. The waterway is, however, part of a busy sea lane carrying enormous quantities of international trade.”
Disclosure of the East China Sea incidents came about seven weeks after the United States publicly accused China of deliberately aiming lasers between two and ten times at military aircraft in Djibouti, in East Africa. In those incidents, the Pentagon said “military-grade” lasers were used. Two U.S. Air Force pilots received minor, unspecified injuries with no long-term effects.
From the Wall Street Journal, news.com.au and Stars and Stripes
Commentary from LaserPointerSafety.com: About 24 laser/aircraft incidents over nine months from boats or the shore of the East China Sea seems like a plausible number for random, unconnected civilian misuse of commonly available laser pointers.
Consider that the East China Sea has an area of about 500,000,000 square miles. This is roughly equivalent to the combined area of Texas, California and Florida. (Of course the Sea is far less populated even considering seacoast populations.)
In the U.S. in 2017, there were roughly 5,600 reported incidents over nine months, so 24 incidents in the same period is a reasonable number for a less-populated area. Another indication that these may be from civilian misuse is that U.S. officials indicated the East China Sea incidents occurred from “smaller, commercial-grade” lasers which includes readily available low-powered consumer laser pointers.
However, if Chinese fishing fleets are a “militia” as claimed by one news source, then there may be some coordination or central control for the laser attacks.
For a contrary view, see the June 25 2018 column “China is Trying to Bring Down American Planes With Lasers. Time to Get Tough” in the Daily Beast. Author Gordon Chang considers but rejects the unorganized attack hypothesis. He says “it is difficult to believe that Chinese fishermen can pick out American military aircraft from civilian ones without radar or other help. Moreover, state support is the best explanation for the increasing sophistication of the laserings.”
Chang argues that “Washington should consider the attacks, almost certainly directed by Beijing, as attempts to injure pilots and their crews. The American response, therefore, should be immediate in timing and devastating in effect….”
Bosnia: US helicopters hit four times by lasers; caused eye injuries
Intro: The pilot and a crewman on an American helicopter were hurt recently (October 24 1998) when someone fired a laser at their aircraft patrolling over Bosnia-Herzegovina. The men were able to land safely but this, and similar incidents in the Balkans, have sparked concern among U.S. air crews. U.S. military officials and police in Bosnia are investigating the incidents, and the U.S. Army says it is now changing the way it uses its helicopters. VOA's Jim Randle reports from the Pentagon.
Text: Pentagon officials say U.S. helicopters have been hit by lasers four times in Bosnia. Officials say one case caused 'mild to moderate' eye injuries when the laser light stayed on the aircraft for four or five seconds. The pilot and a sergeant were both treated for eye injuries, and both are expected to recover and be able to resume flying.
Nevertheless, Pentagon officials say the Army is changing the way It uses helicopters over Bosnia to lessen the danger to pilots -- but will give few details.
Pentagon spokesman Mike Doubleday did say pilots now have some protection from the laser threat: "What we've done to deal with the situation is to provide helicopter crews with either special glasses or goggles that protect their eyes in these situations."
An expert in weapons technology says the pilots have good reason for concern. John Pike studies strategic issues for the Federation of American Scientists. He says four thousand Iranian soldiers suffered eye injuries, including blindness, when Iraqi forces swept powerful lasers across their ranks during the Iran-Iraq War.
Mr. Pike said, "It was a lot easier for them to injure those soldiers using a laser than it was to kill them by hitting them with a bullet. And the thing is that an injured soldier is a lot more of a burden to a military than a dead soldier is, because every injured soldier requires several more to get him back to the hospital."
Mr. Pike says the Iranian battlefield lasers were those used by tanks to determine the range to a target. Other lasers are used to guide bombs and shells to targets with great precision.
Lasers are used by many nations, including the United States, in tanks, anti-aircraft weapons and to disrupt electronic devices.
Mr. Pike says recent treaties [the Protocol on Blinding Laser Weapons, a 1995 amendment to the 1980 Geneva Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons] labeled weapons specifically designed to blind soldiers as "inhumane" and banned their use. But he says with so many lasers playing so many battlefield roles, it will be difficult to enforce the ban on these weapons.
From the Federation of American Scientists
China: Pentagon made "groundless accusations" about Djibouti lasers
According to China Daily, “The Defense Ministry said in a statement that the ministry has dismissed such ungrounded accusations from some US officials via official channels. It added that China always firmly honors international laws and regulations in Djibouti, and is dedicated to safeguarding regional security and peace.”
Separately, Reuters reported that “Chinese Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Hua Chunying said the government had conducted ‘serious checks’ and told the U.S. side the accusations were groundless. ‘You can remind the relevant U.S. person to keep in mind the truthfulness of what they say, and to not swiftly speculate or make accusations,’ she told a daily briefing in Beijing.”
From China Daily and Reuters
US & Djibouti: UPDATED - Pentagon says Chinese have aimed lasers at US planes in Djibouti, causing two injuries
Spokesperson Dana White said the reason for the laser activity is unknown, “but it’s serious, we take it seriously.” She said it was “a true threat to our airmen”. The U.S. has protested and has asked the Chinese government to investigate.
Another Pentagon spokesperson, Major Sheryll Klinke, said the C-130 pilots were hit with a “military grade” laser.
On April 14 2018, the US military posted this notice to airmen (NOTAM) on the Federal Aviation Administration website, warning about “unauthorized laser activity” in Djibouti.

The NOTAM was scheduled to expire on June 14.
The NOTAM coordinates (N1135.70 E04303.14) are about 2,400 feet from China’s military base in Djibouti, opened August 1 2017 near Camp Lemonnier.
An article in the quasi-official South China Morning Post referred to “Chinese military observers [who] said the lasers might have been used to scare off birds near the airfield or disrupt possible spy drones, rather than targeting foreign pilots. A Beijing-based military analyst said China has already demonstrated laser weapons being used against drones, at airshows.
China is a signatory to the Protocol on Blinding Laser Weapons, which bans the use of lasers that cause permanent blindness. The protocol does not ban laser dazzlers, which temporarily impair vision but do not cause eye damage. It is also permitted under the Protocol to use lasers to disrupt or damage cameras and sensors such as those on missiles or satellites.
According to The Drive, “As of 2015, Chinese forces had access to at least four different man-portable systems, the BBQ-905, PY131A, PY132A, and the WJG-2002, all of which look like oversized assault rifles or shoulder-fired grenade launchers.”
From The Drive, Janes 360, C4ISRNET, Defense News, South China Morning Post, FAA PilotWeb, and a YouTube video of the May 3 2018 Pentagon press briefing by Dana White. Thanks to Greg Makhov for bringing this to our attention.
UPDATED May 4 2018: China’s Defense Ministry and Foreign Ministry both denied the U.S. allegations of laser use by China.
UPDATED May 7 2019: An annual report to Congress on Chinese military and security developments does not mention the April 2018 Djibouti laser incidents. It does mention "a few provocative Chinese military actions" but not the alleged Chinese lasers in Djibouti. A news story says the omission is "an apparent bid to preserve the controversial military exchange program with Beijing." From the Washington Free Beacon
US: Military says Soviet ship aimed laser at US aircraft; injuring pilot's eyes
The incident happened September 30 or October 1, 1987. According to an October 2 1987 Pentagon statement, a U.S. Navy P-3 reconnaissance aircraft was “illuminated by an intense light” from the Soviet ship Chukotka. An Air Force WC-135 intelligence plane also was illuminated.
The statement said the light “disturbed” the vision of the co-pilot, and “although preliminary medical evaluation has shown no apparent damage, further detailed tests may be required to determine if, in fact, no damage to her eyes occurred.”
Sen. Malcolm Wallop (R-Wy) initially disclosed the incident. He said “In my opinion, anything that disturbs your vision for 10 minutes damages your vision. The effect was to temporarily blind that co-pilot."
According to the Pentagon, they believe the light source was a laser. The Pentagon statement did not speculate on the reason for the illumination of the aircraft.
The New York Times referenced one official who said the Soviet ship might have tried to harass or blind the pilots, while a naval consultant said it could be that the laser was used to track missiles and was inadvertently shined at the U.S. aircraft.
Such illumination had occurred before, according to the Pentagon statement.
The 1987 edition of a Pentagon publication, Soviet Military Power, said that "recent Soviet irradiation of Free World manned surveillance aircraft and ships could have caused serious eye damage to observers." The following picture and caption appeared on page 113 in the book:

From the New York Times and the Los Angeles Times
Ukraine: Video shows Russian soldier aiming laser at recon plane
The propeller plane was patrolling the northern part of Crimea when it was fired upon during daylight hours.

A still frame from the video, showing the soldier outside a tent
From The Aviationist
US: DOD confirms eye injury to copter passenger; perhaps from Russian vessel Kapitan Man?
Coast Guard and Navy personnel boarded the vessel on April 7 but were unable to find any laser device, or evidence of a possible device. U.S. Navy Lt. Cmdr. Jack Daly was then examined by military laser eye injury experts, who found “there was a high probability that the minor burns on the lieutenant's right retina were caused by multiple laser exposures such as might result from a single glimpse at a repetitive pulsed laser.”

The American naval officer took this photo in the Strait of Juan de Fuca showing a red light on the M/V Kapitan Man. The light led some to suspect a laser. However, subsequent inspection did not find a laser, and in the location of the red light were “two deep red running lights … that met the guidelines established for sidelights.”
The U.S. Defense Department concluded that “[a]vailable evidence does not indicate…what the source of such an exposure might have been. Specifically, there is no physical evidence tying the eye injury of the American officer to a laser located on the Russian merchant vessel.”
The Strait of Juan de Fuca laser incident was also discussed in the August 2004 medical journal Archives of Ophthalmology. The article “Assessment of Alleged Retinal Laser Injuries” describes “Case 5” and concludes that “…[n]o evidence of laser injury was found in the years after the incident by 17 other ophthalmologists, including 5 neuro-ophthalmalogists and 8 retina specialists. A trial was held 5 years after the incident in which the retina specialist who made the initial diagnosis steadfastly maintained all the photographer’s [naval officer’s] symptoms were due to retinal laser injury. A jury ruled against the photographer’s claim for damages against the ship’s owner.… The patient had real complaints, but they were caused by preexisting autoimmune problems rather than by laser injury.”
The full text of the DOD press release, and the “Case 5” study is below (click the “Read More…” link). Additional information above is from a 2011 Washington Times story.