Home
A comprehensive resource for safe and responsible laser use
Canada: Pilots want lasing aircraft to be a crime
Tim Perry made his proposals May 11 2020 after a Jazz Aviation pilot was hospitalized due to being illuminated by laser light on approach to Ottawa/Macdonald-Cartier International Airport, on February 15 2020. The laser source was about three nautical miles from the aircraft. The co-pilot of the de Havilland DHC-8-300 passenger aircraft had to turn control over to the captain, who was able to land without incident. The co-pilot was taken to hospital as a precaution due to actual or potential injuries. No additional information was made available by Jazz due to privacy restrictions.
Perry said that other Canadian aviators have actually suffered permanent retinal damage as a result of laser strikes, according to the National Post. Details on the Jazz pilot's condition, or on the other pilots — how many, degree of severity, eventual outcome — were not listed in the Post article. There were eye injury claims in February 2020 when an Ornge medical support aircraft was struck by a green laser in downtown Toronto, and an eye injury claim by a WestJet pilot flying from Newfoundland to Orlando in May 2019.
The article stated that "Most of the reports in the CADORS [aviation incident] database indicate that police were notified, but neither Transport Canada nor the RCMP [Royal Canadian Mounted Police] could cite an example of anyone in Canada ever being prosecuted." [Note: LaserPointerSafety.com has found at least four cases of Canadian prosecutions.]
Canada has previously taken steps to reduce laser/aircraft incidents. These may be having some effect, as laser incidents have been dropping from a reported high of 658 in 2015, to 274 in 2019, according to the National Post article.
On June 28 2018 Transport Minister Marc Garneau banned the use of hand-held lasers 1 milliwatt or more (the power of a small pet laser pointer) in Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver, and within 10 km of airports or heliports. There are exceptions for uses such as work, education, school or astronomy.
Any person with a battery-operated, handheld laser in a prohibited zone 1) outside of a private dwelling and 2) without a legitimate purpose can be fined immediately and “on the spot” up to CDN $5,000. A corporation violating the law can be fined up to CDN $25,000. The fines are in addition to any criminal prosecution; intentionally aiming a laser at an aircraft can result in five years in prison and/or up to CDN $100,000 in fines.
On May 24 2016, Garneau announced a social media awareness campaign. This included setting up a webpage in June 2015 that includes a catchy animated video, “Dumb Ways to Blind” aimed at millennials, plus three other more conventional videos on the topic. Transport Canada also tweeted using the hashtag "#NotABrightIdea".
Section 7.41(1) of Part I of the Canadian Aeronautics Act is a general prohibition against behavior that endangers aircraft. It provides a fine of up to CDN $100,000 and up to five years in prison for interfering with the duties of a crew member. This has been cited by Transport Canada as part of its webpages discouraging persons from aiming at aircraft.
From the National Post, March 11 2020. Note that there has been a discrepancy between newspaper reports of the number of annual laser/aircraft incidents, and Transport Canada figures. For more information, see the Canada section on the Laser/aircraft illumination statistics page. Thanks to Randy Paura for bringing this news to our attention.
US: Advisory committee recommends pilot procedures, training and glare protection
ARP6378™ has three main parts:
- A description of how lasers can interfere with pilots’ vision and operational performance, and how pilots can reduce adverse effects.
- A recommendation for pilot training, including exposure to safe, simulated laser light in a simulator or other realistic flying environment
- A description of Laser Glare Protection eyewear and windscreen film, with recommendations for whether and how to use these.
The document was developed by the SAE G10OL “Operational Laser” committee over a two-year period. It is available for purchase from SAE for $78. A three-page preview, which includes most of the Table of Contents except the appendices, is here.
From SAE ARP6378™, “Guidance on Mitigation Strategies Against Laser Illumination Effects”, published June 2 2018. Available from SAE.org.
Click to read more...
Canada: Looking at "all possible options" to fight laser incidents; perhaps a ban and mandatory labels
The statement came after six laser incidents over two days earlier in the month, at Montreal’s Trudeau Airport. Garneau said these made him “very, very mad.”
A Transport official said the options include a ban on importation of powerful lasers, mandatory warning labels, and stronger penalties for those who are caught.
Garneau noted that it is hard to catch a laser perpetrator, making prosecutions “few and far between”. He believes that some people are not aware of the bright-light danger of laser light, but that others “know darn well what they’re doing” and are trying to “provoke something.”
Transport Canada currently has a program called “Not-a-Bright-Idea,” trying to educate the general public about the risks and legal consequences of aiming lasers at aircraft. Since implementing the program in May 2016, laser incident numbers have dropped. There were 590 reported incidents in 2015, 527 in 2016, and 379 in 2017.
Garneau said that despite the 28 percent drop, Transport Canada must do more, and that is why they are exploring other options.
From 660 News and AVweb
Note: In response to a LaserPointerSafety.com request, an email address for interested persons was provided: “Transport Canada is exploring options to reduce laser strikes. Canadians and industry members can provide information to the Civil Aviation Communications Centre by emailing: services@tc.gc.ca”
UK: "Call for evidence" response summarizes many groups' views on laser eye, plane incidents; sets forth actions
The U.K. government published on January 8 2018 a 14-page report on laser pointer safety and potential regulation. The report includes two new actions the government will take to reduce the number and risk of unsafe laser pointers:
1) “strengthening safeguards to stop high-powered lasers entering the country”, and
2) “working with manufacturers and retailers to [voluntarily] improve labeling.
Separately, the U.K. government published the Laser Misuse (Vehicles) Bill on December 20 2017. This makes it illegal to point a laser at vehicles, with a prison term of up to five years and an unlimited fine.
“Laser pointers: call for evidence - government response”
From August 12 to October 6 2017, the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy opened a “Call for Evidence” consultation. BEIS set forth 19 questions, asking the public to give their views on laser pointer hazards and what actions to take.
The January 8 2018 government response summarizes the 265 responses received.
The report is especially useful because it incorporates the views of many disparate groups: pilots (64% of respondents), “concerned members of the public” (14%), professional laser safety advisors (9%), users of laser pointers (6%), ophthalmologists (6%), and Trading Standards authorities (2%).
The report then distills these views, finding surprising commonality. It is a good overview for the non-expert on two topics:
1) Actual laser pointer hazards — separating fact from fear
2) Potential actions to reduce the number and severity of laser pointer injuries and incidents — including what actions may not work (e.g., licensing).
We have summarized the findings below (click the “read more” link). However, reading the complete document is well worth the time of anyone interested in this issue.
Click to read more...
US: Survey paper says "Injury from laser pointer trauma is a public health problem on the rise"
It begins by summarizing misuse in sports, and in the thousands of incidents per year in the U.S. where lasers are aimed at aircraft.
The authors, Dr. Gregory D. Lee and Dr. David R. Lally, then write “Perhaps the greatest concerns are raised by reports of unsupervised children who have received these lasers as toys or gifts and expose themselves to the laser beams, causing permanent retinal injury with reduced central vision. From 2000 to 2009, there were five reports of 18 patients with injuries due to laser pointer exposure.”
They discuss the types of injuries (thermal, photochemical and mechanical) and locations of retinal injuries. There is a listing of laser classes, with “pointers” — Class 1, 2 or 3R (IIIa) — being distinguished from similar-looking but more powerful Class 3B and 4 “handheld” lasers.
The authors conclude as follows:
“Inappropriately used class 3B or 4 lasers should be considered weapons that can cause serious, permanent bodily injury. Even brief exposures to diffused rays of laser beams can cause temporary flash blindness that may last for hours in airline pilots, endangering the lives of passengers, particularly during takeoff and landing sequences. Cases of short-range laser exposure are becoming more common, often involving children who are inappropriately given these devices as toys, and these patients are referred to retina specialists after the damage has already occurred.
“No definitive experimental study, case report, or animal model has shown improvement in these injuries with any type of treatment, but typically these patients are treated with a short course of corticosteroids or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Secondary choroidal neovascularization has been treated successfully with intravitreal anti-VEGF agents.13,14
“Clinicians, particularly retina specialists, can raise awareness of this rising public health issue by educating patients and parents about the hazards of laser pointers. Legislation is currently being written to impose stronger regulations on the distribution and sale of these devices. If a patient presents with findings of a laser-related retinal injury, clinicians should report the incident to the FDA so that investigations can be performed into the manufacturers of these devices. Reports can be made at www.fda.gov/downloads/AboutFDA/ReportsManualsForms/Forms/UCM236066.pdf.”
From Retina Today
Northern Ireland: "Laser Lunacy" drama visits schools to warn students not to aim lasers at aircraft
According to an October 19 2016 story in the Irish News, the performance depicts an aircraft crew member being blinded, which leads to a crash that injures 17 people. The subsequent investigation highlights how a criminal conviction can ruin a young person’s life.
After the performance there is a question-and-answer session to reinforce the message.
BIA’s Jaclyn Coulter told the newspaper “We have a very serious message to get across to young people and we thought that the most effective way of doing that was through drama…. [W]e are delighted with the response we have had both from schools and pupils. We want this practice to be stamped out. It is not fun. It is not a game.”
There were 35 aircraft illumination incidents last year, and 16 thus far in 2016.
From the Irish News
UK: Consumer lasers hazardous up close, but will not injure pilots, say 3 top UK experts
But in addition to this declaration, the authors also provided a succinct summary of the current state of consumer laser pointer misuse, and how ophthalmologists should proceed when studying a patient’s laser exposure.
Experts John Marshall, John O’Hagan and John Tyrer began by noting that low-powered Class 2 (less than 1 milliwatt) and Class 3R (1-5 mW) lasers “are not an eye hazard, and even if used inappropriately will not cause permanent eye damage.”
However, consumer laser devices with Class 3B (5-500 mW) and Class 4 (above 500 mW) powers have begun to cause injuries. “….[C]lass 4 devices are capable of causing irreversible retinal damage if directed into the eye over short ranges, up to several metres. Such devices have resulted in foveal injuries in children with current estimates of 150 cases in the UK. The [UK] media has given significant coverage to this growing problem.”
Ophthalmologists were advised that in cases of close up exposure, there may potentially be permanent damage. A detailed examination would be warranted, although there is no treatment to reverse permanent damage.
The hazards from this short range misuse differ from the hazards of aiming a laser towards pilots. Because the laser-to-aircraft distance is typically “hundreds to thousands of metres”, and because of scattering from the windscreen, eye injuries are nonexistent: “Fortunately, these exposures are at irradiances that are incapable of producing irreversible retinal damage even at distances of 100 m.”
They said that only one case of alleged retinal damage has been reported in pilots. [LPS.com note: this is for publicly available reports involving civilian pilots.] The experts concluded the case is suspect for a number of reasons; they do not believe laser targeting caused the alleged injury.
Marshall, O’Hagan and Tyrer turned from injuries to the hazards of distracting pilots with bright laser lights: “Obviously, if such a distraction occurs at a critical time such as during landing then the result could be devastating.”
For ophthalmologists examining pilots, if there are no permanent abnormalities on an Amsler grid test, the physician should not do any detailed eye exam, as this “would only serve to compromise the pilot's vision for a longer period.” The authors noted that pilots may delay seeing an expert for “many hours or a day or so during which there may be a growing psychological element.”
In an interview with CNN, Marshall said the findings on pilot hazards are based on previous laser safety research as well as a new study done with field experiments at a military base over about three years.
In the BJO editorial, the three experts agreed that current laser safety standards and guidelines are based on valid experiments and science. The standards do not need to be revised, “…but clearly further attempts must be made to educate the public.”
The editorial concluded “The European Commission has mandated the European Standardisation bodies to produce a standard specifically for consumer laser products. This should allow enforcing authorities to remove unsafe products from the market. However, compliance by manufacturers will remain an issue, as will direct imports by the public purchasing unsafe laser products over the internet.”
From the British Journal of Ophthalmology editorial “Eye hazards of laser ‘pointers’ in perspective” by John Marshall, John O’Hagan, and John Tyrer, available in HTML text and as a PDF document. Click on the blue “Read More…” link below for an April 19 2016 press release from the BJO summarizing the paper’s findings relative to pilot hazards.
Click to read more...
US: Aviation reporter says FAA anti-laser efforts aren't working; wants more social media
Negroni began the segment by noting that laser incidents are “truly a menace and it’s not to be taken lightly.” She said offenders “don’t watch the news, they don’t read the paper” and thus “they need to be reached out on their level. And that level is like a Facebook level or a Twitter level, where people are actually going to learn.”
She concluded that “it’s just time for the establishment to get on board, before something really terrible happens.”
Negroni has written aviation articles for publications such as the New York Times and Smithsonian Air & Space, is an on-air expert for ABC, CNN and NBC, and has a book on mysterious aviation accidents coming out in 2016. She previously wrote an article for RGN critical of FAA laser publicity efforts entitled “No let-up in laser attacks on airplanes” published December 13 2013, and a blogpost on the same topic on August 28 2014.
From the Runway Girl Network podcast episode 27, “Crash Investigations and Laser Incriminations”, uploaded August 29 2015. A transcript of the laser-relevant parts of the podcast is below.
Click to read more...
South Africa: Students warned not to bring lasers to school
It was unclear from news reports whether the warning was sent directly to students at school, or if the warning came only as part of a May 4 2015 news story on the website Health24.com. A May 11 search of the Gauteng Department of Education website did not show any announcements, notices, documents, or other information warning about laser pointer hazards.
The spokesperson said that at least two children had permanent eye damage from lasers. One case cited was a South African 11-year-old boy who looked into the laser light after one of his classmates was playing with it. His mother said “He now has a blind spot right in front of him, but still see the sides of the eye [sic].” This case was reported in April 2015. The other South African case involved a child who aimed a laser’s light into his eye and had permanent damage.
Gautang is the most populous province in South Africa. It contains the cities of Johannesburg, Pretoria, Midrand and Vanderbijlpark.
From Health24.com: Story about the warning to learners, and story about the 11-year-old boy being injured.
US: UPDATED - Reporter questions effect of FAA/FBI "blame and shame" campaign
She disagrees with the U.S. government’s primary focus being a “blame and shame” campaign that tries to capture laser perpetrators using helicopters, then prosecutes them and publicizes the resulting multi-year sentences. Negroni calls this a “high-tech, heavy-metal, dollar-intensive approach to the problem … [that] has gone terribly wrong…”
Her contention is that persons who aim at aircraft “don’t watch television news, read the daily newspaper or log on to the FAA laser education website before heading out into the night with their nifty green or blue laser pointers.”
She ends her blog post by calling for creativity to try to market this message to its target audience of teens and young men, using a more sophisticated publicity or social media effort.
In the past few years Negroni has written about what she calls “this disaster in the making” for the New York Times, MSNBC, and the Smithsonian’s Air & Space magazine. Late in 2013, she wrote a more detailed article for the blog Runway Girl Network, exploring the problem — and suggested solutions — in more depth.
From Flying Lessons. Background information disclosure: LaserPointerSafety.com provided some information to Negroni which was used in her articles.
UPDATED September 8 2014 - Negroni’s blog post was reprinted by the Huffington Post.
US: Video PSA uses Internet meme to teach laser safety

In the video, various animated characters are shown lasing planes and going to jail, hurting themselves by misusing powerful lasers, aiming at police and getting shot, and otherwise having an ironic, unfortunate outcome.
”Dumb Ways to Blind” is modeled after “Dumb Ways to Die”, a November 2012 YouTube hit originally done for Metro Trains in Melbourne, Victoria. The Australian campaign “generated at least $50 million worth of global media value in addition to more than 700 media stories,” according to ad industry magazine The Age. It was viewed on YouTube over 84 million times as of July 2014.
The laser version is one of dozens of parodies and spin-offs. Unlike many of these which are done only for humor, “Dumb Ways to Blind” appears to have an educational goal similar to the original “Dumb Ways to Die”.
US: FBI expands laser education & reward campaign nationwide for 3 months
The original FBI education and reward program ran from February 11 to April 11 2014 in 12 U.S. cities that had high rates of laser/aircraft incidents. The FBI said the program led to a 19 percent decrease in lasing reports.
The new, nationwide program was announced June 3 2014. The $10,000 reward offer is scheduled to last for 90 days; until September 1.
The FBI said they are working on the educational campaign with the Federal Aviation Administration, the Air Line Pilots Association, International, and state, local and international law enforcement. They are outreaching to schools, teaching teens to not aim at aircraft.
Click to read more...
US: FBI offers $10,000 reward; warns public about laser pointer misuse
This comes as part of a publicity campaign by the FBI to inform the public and especially teenagers about the dangers of lasing aircraft. The agency said teens are the primary age group responsible for laser/aircraft illuminations.
[Note: There appear to be no official records of perpetrators’ ages. However, here are lists of incidents recorded in LaserPointerSafety.com news items, based on the age of the perpetrator: 10-19, 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59, 60-69. Counting the stories in each group may give a rough indication of the age distribution of laser perpetrators.]
The two-month campaign will focus on 12 cities with large number of incidents. FBI field offices participating in the regional reward program are Albuquerque, Chicago, Cleveland, Houston, Los Angeles, New York City, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Sacramento, San Antonio, San Juan, and the Washington Field Office.
During the campaign, the FBI and the Air Line Pilots Association International will work with Clear Channel Outdoor to hang billboards and issue public service announcements in these cities, warning people that a laser prank can lead to prison.
Click to read more...
US: Professor emails all students at university to remind them of laser safety
Douglas Brandt said that pointers should be labeled as Class 2 [less than 1 milliwatt] or Class 3R [less than 5 mW]. He stated that Class 3B and 4 lasers had the potential to damage the eye and were required to be registered with the State of Illinois.
He urged students to not direct a laser pointer at a person’s eye, and not to use Class 3B or 4 lasers, or unlabeled lasers.
Brandt is the laser safety officer at the university, which has about 11,600 students.
From the Daily Eastern News
US: NIST working to get forensics labs to measure laser pointers for court cases
The effort began when NIST physicist and laser safety officer Joshua Hadler worked with the U.S. Attorney’s office on a 2013 case in Fresno, California. Hadler already had devised a relatively simple and inexpensive way to accurately measure laser pointer powers. (His widely-reported study showed that a majority of pointers exceeded the U.S. limit of 5 milliwatts.)
But power is only one factor of the potential laser hazard. The beam spread, or divergence is another key factor. This is because a wide, high-divergence beam will have its energy spread out more, making it dimmer and less hazardous at a distance than an otherwise equivalent-power laser with a narrower, low-divergence beam.
To tackle this, Hadler used a pyroelectric laser camera to measure the laser’s divergence. From the power and divergence, and knowing the approximate distance to the aircraft from the Federal Aviation Administration incident reports, Hadler was able to calculate the irradiance, or laser power over a given area.
The information helped to get a conviction in the Fresno case. Hadler noted that in the past, “...the vast majority of prosecutions were failing, due in no small part to a basic lack of knowledge about the laser devices on the part of nearly everyone in the trial process, including lawyers, judges, and jury members. What they needed was to be able to acquire and present quantitative data about a device's power and its effects at a specified range that could be used in the judicial process."
Hadler will present a paper on February 21 2014 at the American Academy of Forensic Sciences meeting in Seattle, Washington. The paper, “Output Characterization of Handheld Lasers Used in Criminal Aircraft Illumination,” will discuss the needed measurements and will present ideas for having these measurements be done outside of NIST, in law enforcement forensic labs.
From PhysOrg
Canada: Laser strikes up significantly in Edmonton
A police pilot spokesperson said laser users are not reading the packaging which clearly states not to aim at aircraft. After being caught, "There's been a lot of apologies, a lot of regret, some people not realizing the consequences of what they were doing, and then there's been the far opposite -- I can't believe this is happening, this is ludicrous, this isn't serious, it's just a laser pointer."
The pilot also said that a ban is not the answer: "If it's used properly, it's harmless. It's hard to ban something like that, the sale of it completely if 95% of the general public are using it properly."
He noted that not just police aircraft are being lased. Commercial and private aircraft also are at risk.
Edmonton police helicopter pilots are equipped with safety glasses for use during laser illuminations. They have two pair, one to attenuate red laser light and one to attenuate green laser light.
For details on the two most recent Edmonton incidents, on September 6 and 7 2012, see this LaserPointerSafety.com story.
From the Edmonton Journal and Edmonton Sun. Thanks to Keith Murland for bringing this to our attention.
US: L.A. Sheriff's Dept. puts "Laser Strike" info video on YouTube

To see the video, click this link to YouTube. Following this link should also lead to the bonus content videos.
To get a flavor of the training video, click the “Read More…” link below for a list of selected excerpts and interesting statements.
World: Summary of papers presented at International Laser Safety Conference 2013
Laser pointer hazards for pilots
- A study of the actual output of 40 laser pointers, with powers up to 1.5 Watts, showed significant differences between measured and calculated hazard levels. In some cases, the actual hazard measured at some spots inside the beam was three times the estimated hazard. This is due to the laser output not being smooth in all cases, but instead the beams having “hot spots”. The study also showed that windscreens reduced the beam irradiance -- which is safer for pilots -- from 5% to 60%. (Note however that the McLin study described below showed that windscreens also spread the beam and thus increase glare.)
- A discussion of how being inside the Nominal Ocular Hazard Distance of a laser beam does NOT mean instant blindness for pilots and others.For example, consider a 1 Watt, 1 milliradian laser where the recommended safety distance (NOHD) is 733 feet. If possible, you should be at least 733 feet from the laser before exposing an eye to the direct beam. What is the actual hazard? At 232 feet from this laser, there is a 50/50 chance of the beam causing a barely observable retinal lesion under laboratory conditions where the laser and eye are fixed in place. Due to motion of the aircraft and hand-holding the laser, the chance of a retinal lesion is likely to be less. The distance from 232 feet (“ED50”) out to the NOHD at 733 feet is a known “safety factor” where the chance of retinal injury decreases even further. At the NOHD there is a “vanishingly small risk of hazardous exposure” (Sliney, 2013). Police and other first responder pilots can use this information to better weigh the risk of laser exposure to laser light vs. the benefits of completing a mission (rescuing a person, apprehending criminals, etc.). This presentation also discusses ways to make flight near lasers safer for pilots. A PDF file of all the slides presented is here.
For additional ILSC 2013 papers, click the “read more” link.
Click to read more...
US: New York area officials ask for public's help
A pilot from the Air Line Pilots Association told of his experiences when hit by laser light, and said that “Laser illumination can cause temporary blindness and even permanently damage a pilot’s eyes, potentially leading to an aircraft accident…Individuals must understand the danger and their responsibility to report anyone who misuses lasers.”
The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey is sending officers to schools near airports, to explain the hazards of lasers to children, and to warn them against aiming at aircraft.
An FBI agent said that the bureau is worried about adults and deliberate attacks by terrorists. Fines can range up to $11,000, said an FAA representative. a Coast Guard pilot said that rules requiring helicopters to break off rescues if they are directly lasered, adds to the risk of those the Coast Guard is trying to rescue.
The various law enforcement officials said they were asking the public to call 911 or local authorities if they see misuse, because laser incidents are so frequent and it is rare to apprehend the perpetrators.
A radio station public service announcement has been produced and aired by radio station NJ 101.5. It warns listeners not to aim at aircraft.
From NBC New York and New Jersey 101.5
UK: CAA issues Safety Notice to pilots, after 2,300 laser attacks in 2011
Below are highlights from the document, which gives some background information and statistics, and then describes how affected crew should prepare for and react to a laser attack. (Emphasis in bold added by LaserPointerSafety.com.)
Click to read more...
UK: Eye test for pilots available from CAA website
The ALESA card is available in hard copy, and can also be downloaded from CAA’s website. If downloaded, the Amsler Grid on the first page should be printed so it is 10 x 10 cm.

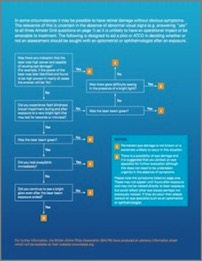
Click for PDF version from CAA ALESA webpage
When staring at the dot in the center of the grid, if the lines appear distorted or there are blank or faded areas, there may be a problem. The person is encouraged to remove themselves from aviation-related duties such as flying or air traffic control, and to see an eye specialist.
The second page has a flowchart of exposure conditions leading either to a “1” meaning unlikely eye damage or a “2” meaning eye damage possibility. If the person scores a “2”, the flowchart suggests they see an eye specialist.
From PilotWeb and the CAA ALESA webpage. The CAA press release about ALESA is here.
US: New "laser strike protection" website and training from Night Flight Concepts.
The company also introduced the Laser Eye Protection Program training course. It is intended to “teach aircrew members the capabilities, limitations and preventative measures required to respond to a laser strike.” The cost is $125; the course takes about an hour and has a test at the end.
[Note from LaserPointerSafety.com: Pilots may also wish to review our online information from the SAE G10T and other sources on how to recognize and recover from laser illumination incidents.]
US: Laser safety training part of UAW/GM labor pact
Due to the potential for catastrophic injuries from lasers, the UAW bargaining team pushed hard to expedite safety training in this growing field. Within 30 days of ratification, the UAW-GM Health and Safety Training Department will schedule a train-the-trainer (T3) Laser Safety Awareness Training course to be taught at the CHR [UAW-GM Center for Human Resources].
From the UAW GM Report via DetroitNews.com